
Stainless Steel Laser Cutting Services
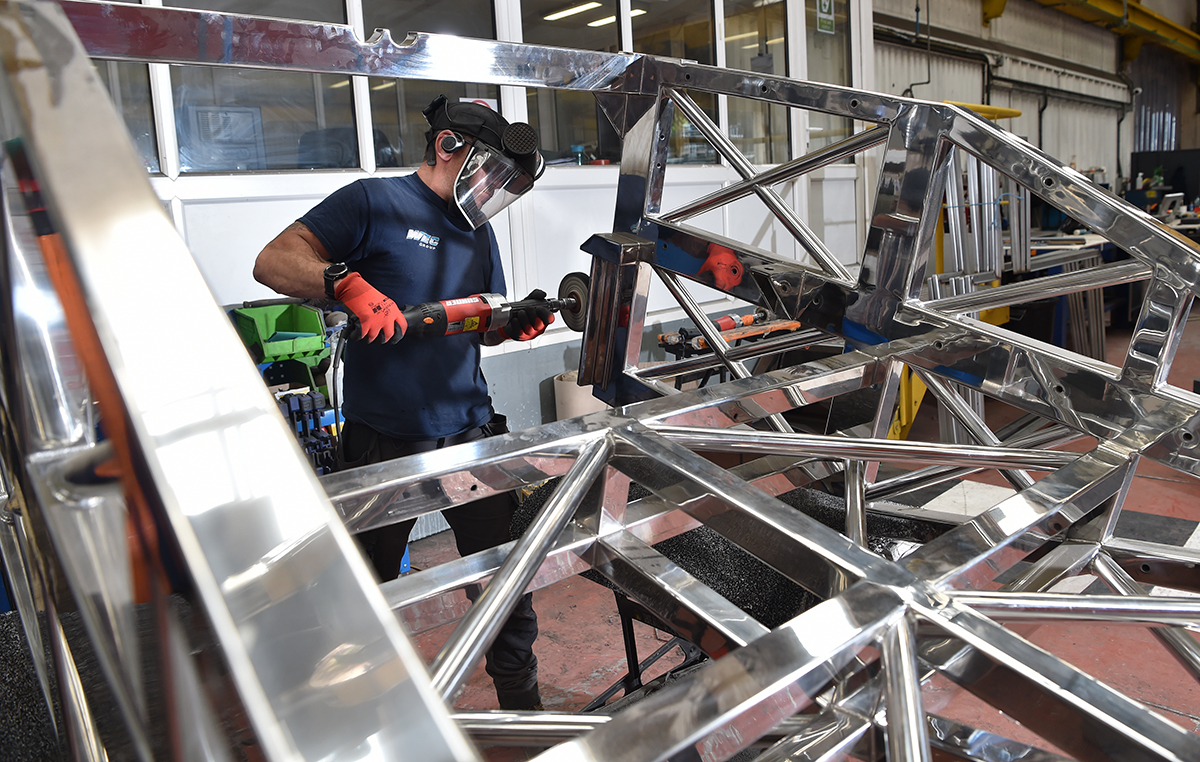
At WEC Laser, we excel in providing top-tier laser cutting services for stainless steel, renowned for its remarkable corrosion resistance, robustness, and longevity. Stainless steel is a crucial material across various industries globally due to its versatile applications.
Equipped with advanced laser cutting technology, our facilities can process a wide range of stainless steel types, handling thicknesses up to 40mm and sheet dimensions up to 4m x 2m. With around-the-clock operations, we are dedicated to completing even the most intricate projects with efficiency and the highest quality standards.
Additionally, we stock and cut most standard stainless steel material grades and thicknesses, including:
- 304 stainless steel
- 316 stainless steel
- Polished stainless steel
- Brush finished stainless steel
- Patterned stainless steel
Stainless Laser Cutting Capabilities
| CUTTING PROCESS | THICKNESSES |
| Flat bed laser cutting | Stainless steel: Up to 40mm |
| Tube, Box Section, Angle and Pipe Cutting | Stainless Steel: 8mm wall thickness |
| High Definition Plasma Cutting | Stainless steel: Up to 50mm |
| Dynamic Waterjet Cutting | Stainless steel: Up to 300mm |
Why choose WEC Laser?
Fast Lead Times
Our Next Day Laser Cutting UK services are designed to meet urgent needs, providing rapid turnaround times for projects requiring immediate action.
Highly Competitive Prices
With our diverse selection of machines, we are able to offer customers the most budget-friendly laser cutting solutions.
State-of-the-art equipment
With 22 flatbed laser cutting machines equipped with automation, our fleet delivers unmatched precision and efficiency.
Experienced Technicians:
We have a team of experts with extensive experience and proficiency in laser cutting stainless steel.
Customised Solutions
We work hand-in-hand with you to understand your unique requirements and offer tailored solutions that meet your expectations.
Rigorous Quality Control
Every project is subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure it adheres to the highest standards.
Precision and Consistency
Our commitment is to provide tight tolerances and consistently high-quality results for every cut, irrespective of complexity.
Certified Excellence
We hold BSI ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 3834 accreditations, ensuring consistent quality and reliability for projects of all sizes and complexities.
Laser Cutting Capacity
As the UK's largest steel processor, we take pride in our cutting-edge facility, which features 22 flatbed lasers, including 12 advanced fibre lasers with fully automated loading and part sorting systems. Our latest addition is a robust 24kW fibre laser, capable of cutting stainless steel sheets up to 8m x 2.5m in size and 40mm in thickness.
Additionally, we operate three fibre tube lasers, designed to handle stainless steel up to 8mm thick, ensuring precision and efficiency across a diverse range of cutting applications.

21
Flat Bed Lasers
24
Press Brakes
2
Tube Lasers
24h
Cutting Capacity
Benefits of Laser Cut Stainless Steel

Cost-Effectiveness
Laser cutting maximizes material usage by producing highly accurate cuts with minimal kerf, resulting in less waste.
Ease of Cutting
The exceptional machinability of stainless steel leads to faster processing times, reduced energy consumption, and improved efficiency.
High Precision
Laser cutting provides high precision and accuracy, achieving tight tolerances and intricate details with minimal deviation.

Versatility
We can cut a wide range of stainless steel thicknesses and grades, accommodating various design requirements and applications.
Minimal Distortion
Laser cutting generates less heat compared to other methods, minimizing thermal distortion and preserving the material’s properties.

Smooth Edges
The process results in clean, smooth edges with minimal need for post-processing, reducing finishing costs and time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Stainless steel comes in several types, each with distinct properties and applications. Here are the main categories:
Austenitic Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: Non-magnetic, highly corrosion-resistant, good formability, and weldability.
- Applications: General-purpose use, resistant to oxidation, often found in kitchen equipment, piping, chemical containers, marine environments, medical devices, and chemical processing.
Ferritic Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: Magnetic, good corrosion resistance, and lower thermal expansion. Less ductile compared to austenitic types.
- Applications: Used in automotive parts, kitchen appliances, and home appliances due to its resistance to oxidation and cost-effectiveness. Also employed in furnace parts and heat exchangers.
Martensitic Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: Magnetic, strong, and hard but less resistant to corrosion compared to austenitic and ferritic types.
- Applications: Suitable for applications requiring hardness and wear resistance, such as cutlery, valve parts, and shafts. Also used in surgical instruments and knives for higher corrosion resistance.
Duplex Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: Combines the properties of austenitic and ferritic types; offers high strength and improved resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
- Applications: Common in the oil and gas industry, chemical processing, marine environments, and extreme conditions such as desalination plants and oil rigs.
Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: High strength and hardness achieved through heat treatment, with good resistance to corrosion and stress corrosion cracking.
- Applications: Used in aerospace, marine, and chemical processing applications for components requiring high strength and toughness.
High-Performance Stainless Steel:
- Characteristics: Designed for specialised applications with extreme conditions.
- Applications: Employed in chemical and petrochemical industries for resistance to sulphuric acid and other corrosive environments, as well as aerospace and high-temperature environments for its resistance to oxidation and corrosion.
Each type of stainless steel has unique properties making it suitable for specific applications, from kitchenware and automotive parts to industrial equipment and medical devices.
- 304: Offers excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and weldability. Commonly used in kitchen equipment, sinks, piping, food processing equipment, and architectural applications.
- 316: Provides superior corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and in marine environments. Typically found in marine equipment, chemical processing, medical devices, and pharmaceuticals.
- 310: Known for its high-temperature resistance and oxidation resistance. Often used in furnace parts, heat exchangers, and high-temperature industrial applications.
- 430: Features good corrosion resistance, is magnetic, and has a lower cost. Used in automotive parts, kitchen appliances, and household items.
- 446: Offers high resistance to oxidation and thermal expansion. Commonly used in furnace components, heat exchangers, and high-temperature applications.
- 410: Provides good hardness and moderate corrosion resistance. Suitable for cutlery, valve parts, and some industrial tools.
- 420: Similar to 410 but with improved corrosion resistance. Often used in surgical instruments, knives, and other applications requiring high hardness and moderate corrosion resistance.
- 440C: Known for very high hardness and wear resistance, with good corrosion resistance. Used in high-performance cutlery, bearings, and industrial equipment.
- 2205: Combines high strength with good corrosion resistance and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. Common in the oil and gas industry, chemical processing, and marine applications.
- 2507: A super duplex grade with high strength and excellent resistance to corrosion and pitting. Suitable for extreme environments such as desalination plants, oil rigs, and chemical processing.
- 17-4 PH: Provides high strength, good corrosion resistance, and hardness. Used in aerospace components, marine applications, and chemical processing.
- 15-5 PH: Similar to 17-4 PH but with improved toughness and corrosion resistance. Often used in aerospace, pumps, valves, and other high-performance applications.
- Alloy 20: Known for its excellent resistance to sulphuric acid and other corrosive environments. Typically used in chemical and petrochemical industries.
- Hastelloy: A nickel-based alloy with superior resistance to high-temperature oxidation and corrosion. Common in aerospace, chemical processing, and high-temperature applications.
Stainless steel can be finished in various ways to achieve different appearances, textures, and performance characteristics. Here are some common finishes:
1. Polished Finishes
- Mirror Finish (No. 8):
- Description: Highly reflective, with a mirror-like surface.
- Applications: High-end architectural features, decorative applications, and premium consumer goods.
- 2B Finish:
- Description: Smooth, reflective surface with a slightly less polished look than mirror finish.
- Applications: Kitchen appliances, industrial equipment, and general-purpose applications.
2. Brushed and Satin Finishes
- Brushed Finish (No. 4):
- Description: Matte finish with fine lines brushed into the surface.
- Applications: Kitchen appliances, elevators, and architectural panels.
- Satin Finish:
- Description: Smooth, non-reflective surface with a soft sheen.
- Applications: Handrails, industrial applications, and some consumer products.
3. Patterned Finishes
- Embossed or Textured Finish:
- Description: Surface features raised or recessed patterns for a decorative effect.
- Applications: Decorative panels, custom architectural features, and high-traffic surfaces.
- Checkered Finish:
- Description: Patterned with a checkered or diamond plate design for enhanced grip and aesthetics.
- Applications: Flooring, industrial applications, and safety surfaces.
4. Specialty Finishes
- Bead Blasted Finish:
- Description: Rough texture achieved by blasting the surface with beads or particles.
- Applications: Architectural elements, decorative items, and some functional components.
- Electropolished Finish:
- Description: Electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material to improve smoothness and corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Food and beverage processing equipment, medical devices, and high-purity applications.
- Anodised Finish:
- Description: Electrolytic process that enhances corrosion resistance and can add colour to the surface.
- Applications: Decorative and functional applications, often in architectural and consumer products.
5. Oxidised and Coloured Finishes
- Blackened Finish:
- Description: Surface is treated to achieve a black or dark appearance.
- Applications: Decorative items, architectural features, and aesthetic applications.
- Coloured Finish:
- Description: Stainless steel is treated to achieve various colours, such as gold, bronze, or blue.
- Applications: Decorative panels, custom architectural features, and consumer products.
Each finish can affect not only the appearance but also the durability, corrosion resistance, and maintenance requirements of stainless steel. The choice of finish often depends on the specific application and desired aesthetic or functional characteristics.
Stainless steel is a highly versatile material used across a wide range of industries due to its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Here are some common uses of stainless steel:
In architectural applications, stainless steel is used for building facades, providing a sleek, modern appearance and durability. It is also used for handrails and balustrades, ideal for both indoor and outdoor railings due to its strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, it is employed in structural components such as bridges and support beams because of its load-bearing capacity.
In the industrial and manufacturing sectors, stainless steel’s resistance to chemicals and high temperatures makes it suitable for chemical processing equipment like reactors, tanks, and pipelines. It is also used in food and beverage processing for equipment like mixers, conveyors, and storage tanks due to its hygienic properties and ease of cleaning. In the oil and gas industry, it is used in pipelines, valves, and fittings that require high strength and resistance to harsh environments.
In the medical and healthcare fields, stainless steel’s corrosion resistance and ability to be sterilised make it ideal for surgical instruments and medical devices. It is also used in orthopaedic implants and dental prosthetics due to its biocompatibility.
For consumer goods, stainless steel is commonly used in kitchen appliances such as sinks, countertops, and refrigerators for their durability and ease of maintenance. It is also used for cutlery and cookware, including knives, forks, spoons, pots, and pans, due to its resistance to staining and rust.
In the automotive industry, stainless steel’s ability to withstand high temperatures and resist corrosion makes it suitable for exhaust systems. It is also used in vehicle trim, bumpers, and other exterior elements for its aesthetic appeal and durability.
In construction and engineering, stainless steel is used for fasteners and fittings such as nuts, bolts, and screws due to their strength and resistance to environmental factors. It is also employed in large-scale infrastructure projects like tunnels and bridges for structural reinforcement.
In the energy sector, stainless steel is utilised in power generation components, including turbines and reactors, where strength and resistance to heat and corrosion are crucial. It is also used in renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines and solar panel mounts, due to its durability and ability to withstand outdoor conditions.
In marine applications, stainless steel is employed in boat and shipbuilding for hulls, decks, and fittings, thanks to its resistance to saltwater and harsh marine environments. It is also used in offshore structures like platforms and rigs where exposure to corrosive elements is a concern.
Each application leverages stainless steel’s unique properties, such as resistance to corrosion, strength, and aesthetic appeal, making it a material of choice in numerous fields.

